Town Žilina
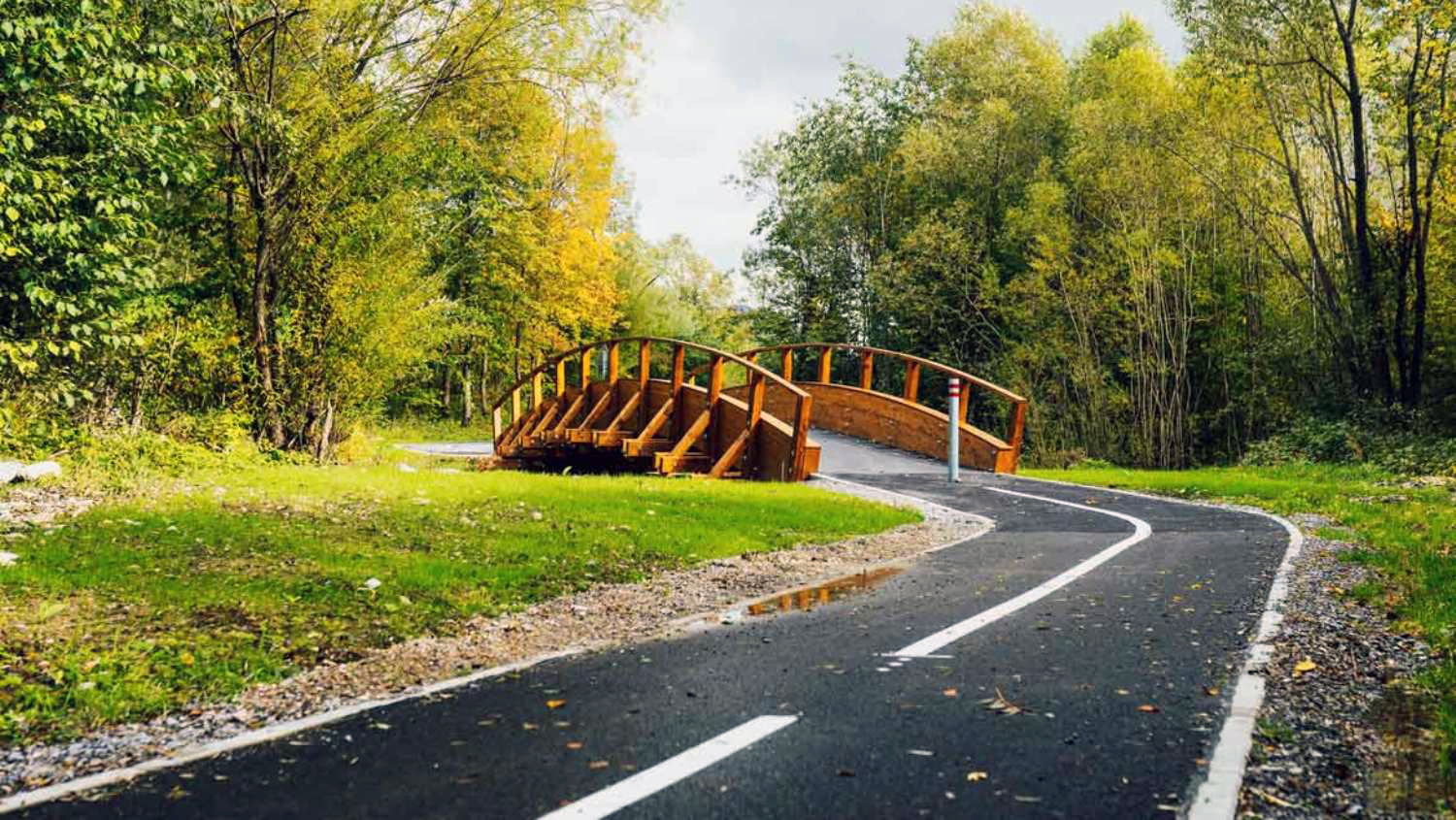
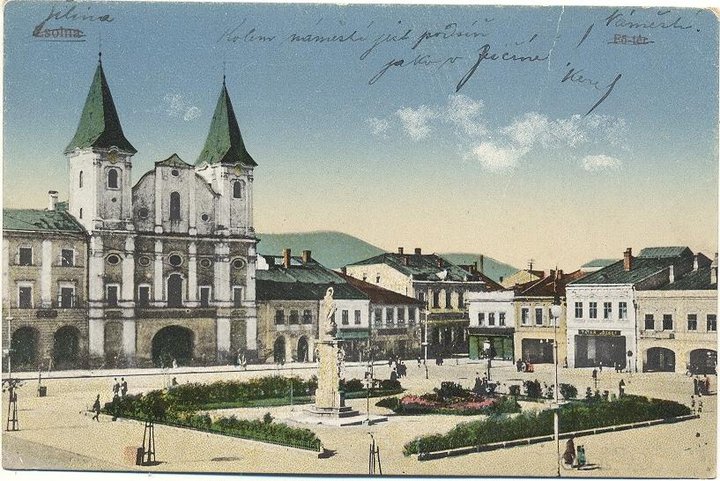
Žilina (Slovak pronunciation: [ˈʒilina]; German: Sillein, [ziˈlaɪ̯n] or [ˈzɪlaɪ̯n]; Hungarian: Zsolna; Polish: Żylina, names in other languages) is a city in north-western Slovakia, around 200 kilometres (120 mi) from the capital Bratislava, close to both the Czech and Polish borders. It is the fourth largest city of Slovakia with a population of approximately 85,000, an important industrial center, the largest city on the Váh river, and the seat of a kraj (Žilina Region) and of an okres (Žilina District). It belongs to Upper Váh region of tourism.
History of Žilina
The area around today's Žilina was inhabited in the late Stone Age (about 20,000 BC). In the 5th century Slavs started to move into the area. However, the first written reference to Žilina was in 1208 as terra de Selinan. From the second half of the 10th century until 1918, it was part of the Kingdom of Hungary.
In the middle of the 13th century terra Sylna was the property of the Cseszneky de Milvány family.[1] The city started to develop around year 1300, and according to records in 1312 it was already a town. In 1321, King Charles I made Žilina a free royal town. On 7 May 1381 King Louis I issued Privilegium pro Slavis which made the Slav inhabitants equal to the Germans by allocating half of the seats at the city council to Slavs.[2] The town was burned in 1431 by the Hussites.
During the 17th century, Žilina gained position as a center of manufacturing, trade and education and during the baroque age many monasteries and churches were built as well as the Budatín Castle. In the Revolutions of 1848, Slovak volunteers, part of the Imperial Army, won a battle near the city against Hungarian honveds and gardists.[citation needed]
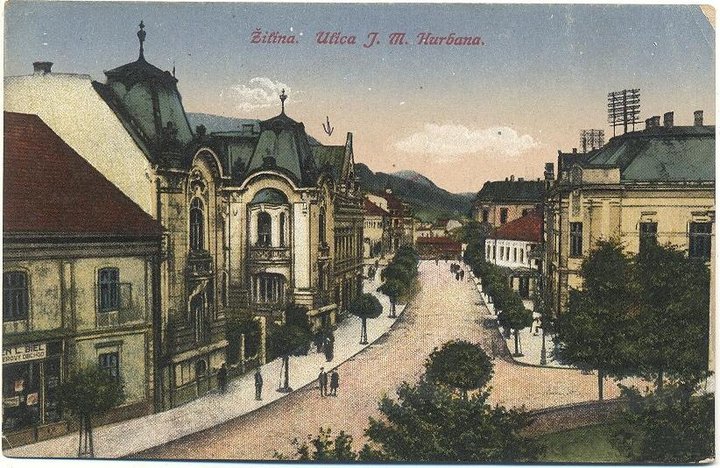
The city boomed in the second half of the 19th century as new railway tracks were built: the Kassa Oderberg Railway was finished in 1872 and the railway to Bratislava (Pozsony in Hungarian) in 1883, and new factories started to spring up, such as the drapery factory Slovena (1891) and the Považie chemical works (1892).
It was one of the first municipalities to sign the Martin Declaration (30 October 1918), and until March 1919 it was the seat of the Slovak government. On 6 October 1938, shortly after the Munich Agreement, the autonomy of Slovakia within Czechoslovakia was declared in Žilina.
During World War II, Žilina was captured on 30 April 1945 by Czechoslovak and Soviet troops of the 4th Ukrainian Front, after which it again became part of Czechoslovakia.
After Second World War, the city continued its development with many new factories, schools and housing projects being built. It was the seat of the Žilina Region from 1949–1960 and again since 1996.
Today Žilina is the third largest city in Slovakia, the third most important industrial center and the seat of a university, the Žilinská univerzita (founded in 1953). Since 1990 the historical center of the city has been largely restored and the city has built trolleybus lines.
Town Žilina
Žilina (Slovak pronunciation: [ˈʒilina]; German: Sillein, [ziˈlaɪ̯n] or [ˈzɪlaɪ̯n]; Hungarian: Zsolna; Polish: Żylina, names in other languages) is a city in north-western Slovakia, around 200 kilometres (120 mi) from the capital Bratislava, close to both the Czech and Polish borders. It is the fourth largest city of Slovakia with a population of approximately 85,000, an important industrial center, the largest city on the Váh river, and the seat of a kraj (Žilina Region) and of an okres (Žilina District). It belongs to Upper Váh region of tourism.
History of Žilina
The area around today's Žilina was inhabited in the late Stone Age (about 20,000 BC). In the 5th century Slavs started to move into the area. However, the first written reference to Žilina was in 1208 as terra de Selinan. From the second half of the 10th century until 1918, it was part of the Kingdom of Hungary.
In the middle of the 13th century terra Sylna was the property of the Cseszneky de Milvány family.[1] The city started to develop around year 1300, and according to records in 1312 it was already a town. In 1321, King Charles I made Žilina a free royal town. On 7 May 1381 King Louis I issued Privilegium pro Slavis which made the Slav inhabitants equal to the Germans by allocating half of the seats at the city council to Slavs.[2] The town was burned in 1431 by the Hussites.
During the 17th century, Žilina gained position as a center of manufacturing, trade and education and during the baroque age many monasteries and churches were built as well as the Budatín Castle. In the Revolutions of 1848, Slovak volunteers, part of the Imperial Army, won a battle near the city against Hungarian honveds and gardists.[citation needed]
The city boomed in the second half of the 19th century as new railway tracks were built: the Kassa Oderberg Railway was finished in 1872 and the railway to Bratislava (Pozsony in Hungarian) in 1883, and new factories started to spring up, such as the drapery factory Slovena (1891) and the Považie chemical works (1892).
It was one of the first municipalities to sign the Martin Declaration (30 October 1918), and until March 1919 it was the seat of the Slovak government. On 6 October 1938, shortly after the Munich Agreement, the autonomy of Slovakia within Czechoslovakia was declared in Žilina.
During World War II, Žilina was captured on 30 April 1945 by Czechoslovak and Soviet troops of the 4th Ukrainian Front, after which it again became part of Czechoslovakia.
After Second World War, the city continued its development with many new factories, schools and housing projects being built. It was the seat of the Žilina Region from 1949–1960 and again since 1996.
Today Žilina is the third largest city in Slovakia, the third most important industrial center and the seat of a university, the Žilinská univerzita (founded in 1953). Since 1990 the historical center of the city has been largely restored and the city has built trolleybus lines.
Žilina Region
The Žilina Region (Slovak: Žilinský kraj; Polish: Kraj zyliński) is one of the eight Slovak administrative regions and consists of 11 districts (okresy) and 315 municipalities, from which 18 have a town status. The region was established in 1923, however, in its present borders exists from 1996. It is more industrial region with several large towns. Žilina is region administrative center and a strong cultural environment is in Martin.
Geography
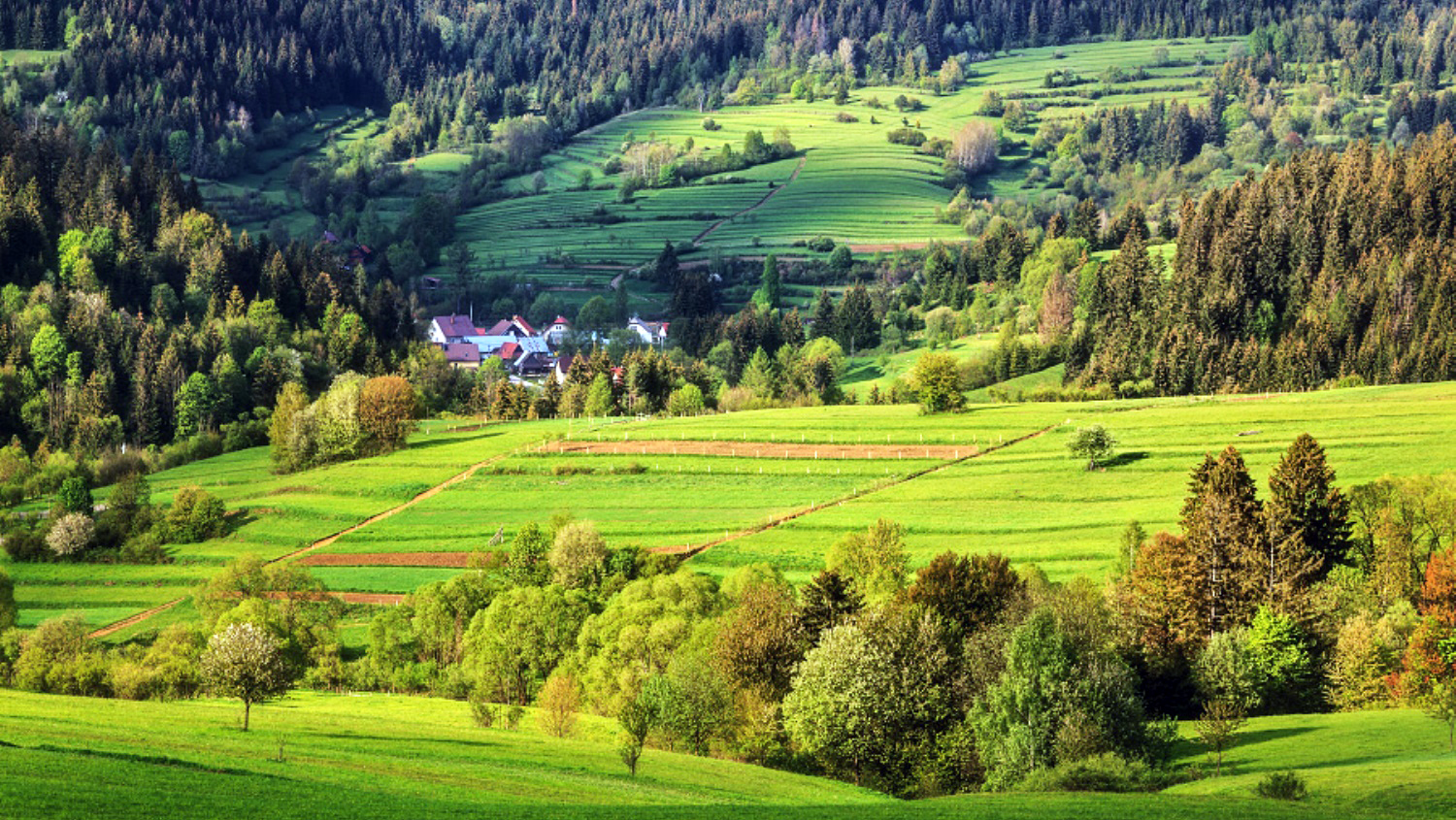
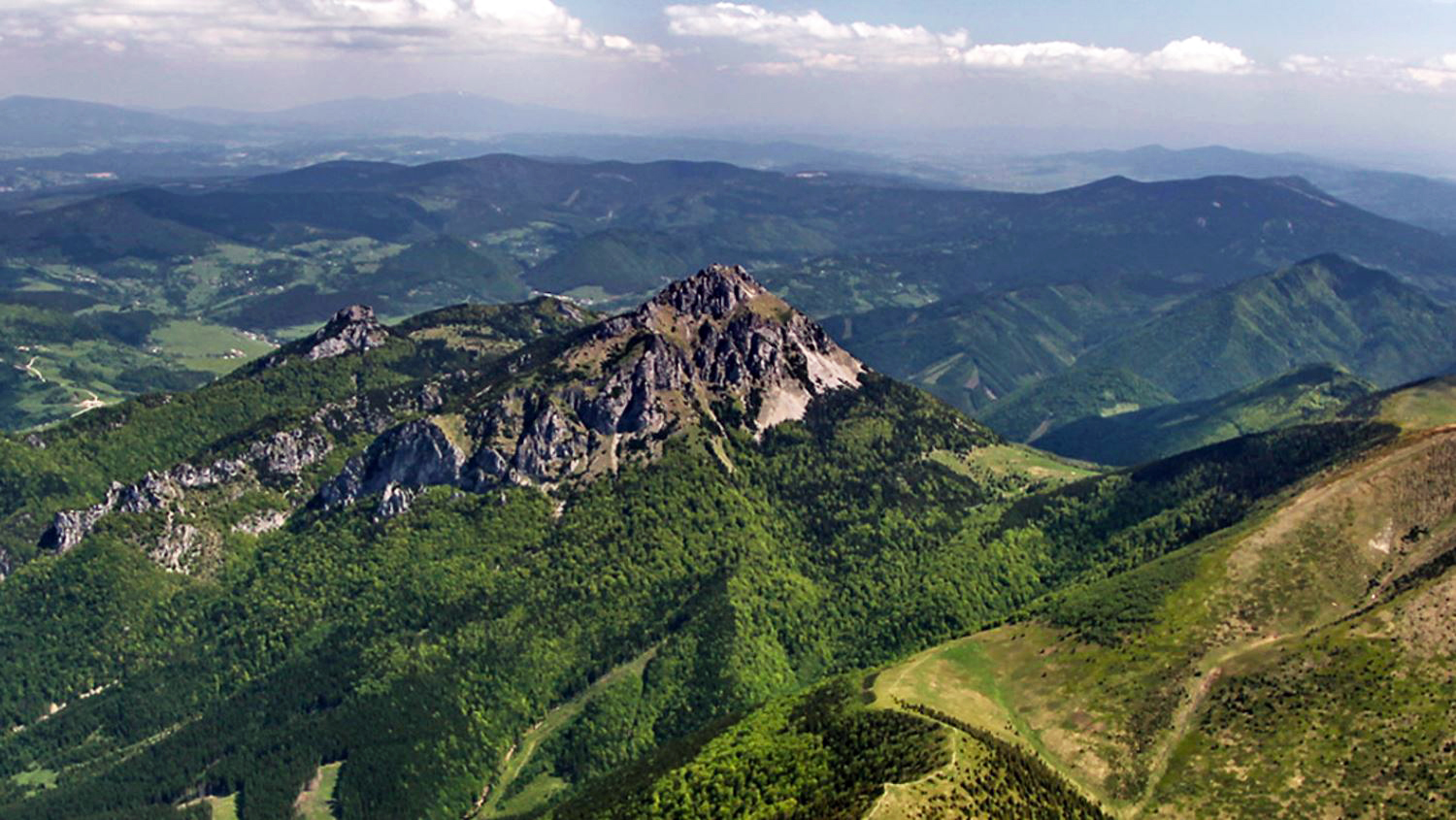
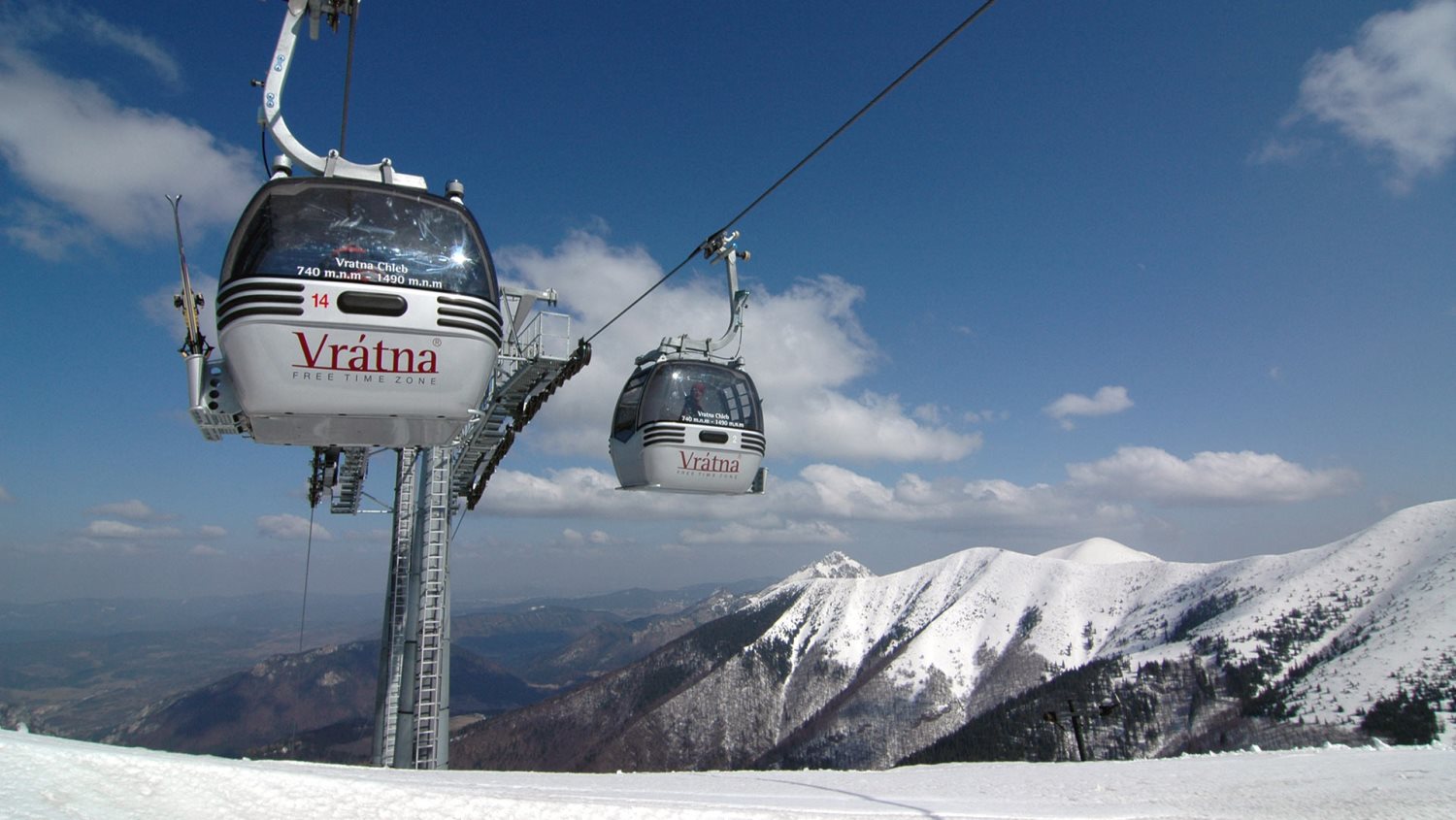
It is located in northern Slovakia and has an area of 6,804 km² and a population of 688,851 (2011). The whole area is mountainous, belonging to the Western Carpathians. Some of the mountain ranges in the region include Javorníky, the Lesser Fatra and the Greater Fatra in the west, Oravská Magura, Chočské vrchy, Low Tatras and Western Tatras in the east. Whole area belongs to the Váh river basin. Some of its left tributaries are Turiec and Rajčanka rivers and its right tributaries Belá, Orava and Kysuca. National parks on the region's territory are the Lesser, Greater Fatra, Low Tatras and Tatra; landscape protected areas are Strážovské vrchy, Kysuce and Horná Orava. The region borders Prešov Region in the east, Banská Bystrica Region in the south, Trenčín Region in the south-west and west, Czech Zlín Region and Moravian-Silesian Region in the north-west and Polish Silesian and Lesser Poland voivodeships in the north and north-east.
History
After the fall of Great Moravia in the early 9th century, the area became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in the 12th century practically to 1918. Before the break it was part of the Hungarian counties of Trenčín, Turiec, Orava and Lipto. After incorporation into Czechoslovakia, the counties continued to exist under their Slovak names of Trenčín, Turiec, Orava and Liptov, but only to 1923, when they were replaced by (grand) counties ((veľ)župy) From 1928 it was part of the administrative unit "Slovak Land". During the WWII Slovak Republic, the area was split between Trenčín and Tatra counties. Since 1928 it was part of the administrative after reincorporation into Czechoslovakia in 1945, the pre-war state was restored. In 1949-1960 there was a unit with the name Žilina Region but it was abolished in 1960 and the area became part of new Central Slovak Region, of which it was part until 1990 (except 1969-70) when it was abolished. After the independence of Slovakia in 1993, the current region was established in 1996. Since the administrative regions became autonomous in 2002, it is governed by the Žilina Self-Governing Region.
Demographics
The population density in the region is 102 inhabitants per km². The largest towns are Žilina, Martin, Liptovský Mikuláš, Ružomberok and Čadca. The level of urbanization is relatively low, with about 50% of the population living in the towns, with the Námestovo District having the lowest urbanization in the whole of Slovakia, only 15%. According to the 2001 census, there were 692,332 inhabitants in the region, almost wholly Slovaks (97.5%), with small minorities of Czechs (<1%) and Roma (<0.5%).[1]
Economy
From the stagnation in the 1990s the region now enjoys relative prosperity. Main employers are industry and tourism. The river Váh valley, which runs across the entire region, forms a strong industrial base with wood pulp and engineering factories as well as Volkswagen and Kia plants in Žilina and Martin.[2]
Slovakia
Slovakia's roots can be traced to the 9th century state of Great Moravia. Subsequently, the Slovaks became part of the Hungarian Kingdom, where they remained for the next 1,000 years. Following the formation of the dual Austro-Hungarian monarchy in 1867, language and education policies favoring the use of Hungarian (Magyarization) resulted in a strengthening of Slovak nationalism and a cultivation of cultural ties with the closely related Czechs, who were under Austrian rule. After the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire at the close of World War I, the Slovaks joined the Czechs to form Czechoslovakia. During the interwar period, Slovak nationalist leaders pushed for autonomy within Czechoslovakia, and in 1939 Slovakia became an independent state allied with Nazi Germany. Following World War II, Czechoslovakia was reconstituted and came under communist rule within Soviet-dominated Eastern Europe. In 1968, an invasion by Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts of the country's leaders to liberalize communist rule and create "socialism with a human face," ushering in a period of repression known as "normalization." The peaceful "Velvet Revolution" swept the Communist Party from power at the end of 1989 and inaugurated a return to democratic rule and a market economy. On 1 January 1993, the country underwent a nonviolent "velvet divorce" into its two national components, Slovakia and the Czech Republic. Slovakia joined both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004 and the euro zone on 1 January 2009.
Location: Central Europe, south of Poland